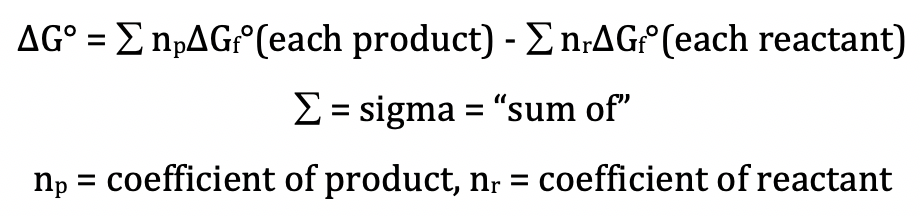Standard gibbs free energy of formation of a compound can be calculated using standard enthalpy of formation δh ƒ absolute standard entropy δs and standard.
Standard gibbs free energy change formula.
The standard gibbs free energy of formation g f of a compound is the change of gibbs free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states the most stable form of the element at 1 bar of pressure and the specified temperature usually 298 15 k or 25 c.
In other words it is the difference between the free energy of a substance and the free energies of its elements.
Gibbs free energy has extensive property and a function with a single value.
In this equation t is the temperature on the kelvin scale.
If we know the enthalpy change h o and the entropy change s o for a chemical process we can determine the standard state free energy change g o for the process using the following equation.
G h ts.
Using enthalpy changes and entropy changes to determine standard state free energy changes.
And we learned in the last video that to answer that question we have to turn to gibbs free energy or the change in gibbs free energy.
Gibbs free energy g.
Delta g zero is the standard change in free energy or the change in free energy under standard conditions.
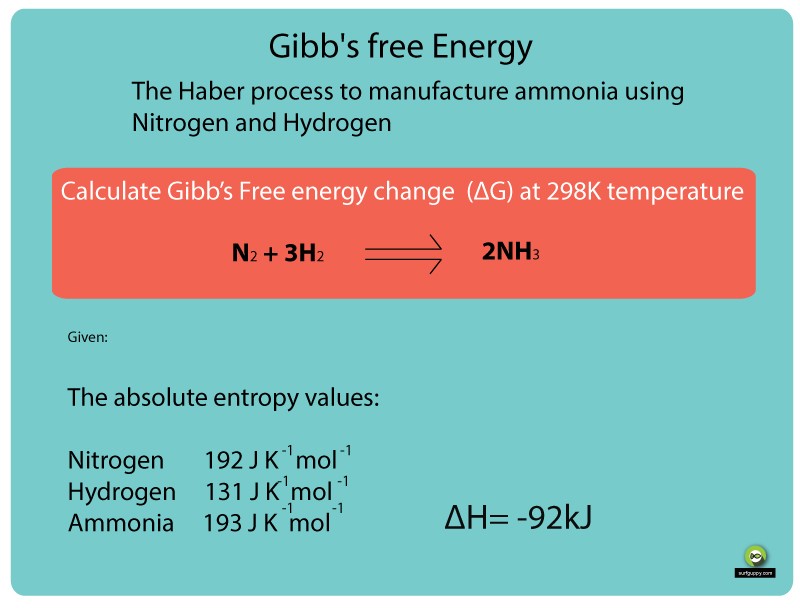
Given δh 74 9kj mol and δs 80 7j k mol.
The change in free energy that occurs when a compound is formed form its elements in their most thermodynamically stable states at standard state conditions.
Delta g zero is equal to negative rt natural log of k.
So we solve for delta g zero.
So we have another very important equation to think about.
R is the gas constant t is the temperature in kelvin and k is our equilibrium constant.
δh change in enthalpy.
Standard state free energy of reaction g.
The gibbs free energy of the system is a state function because it is defined in terms of thermodynamic properties that are state functions.
Standard gibbs free energy of formation is the change in gibbs free energy when elements in their standard states combine to form a product also in its standard state.
The standard gibbs free energy of formation of a compound is the change of gibbs free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of that substance from its component elements at their standard states the most stable form of the element at 25 c and 100 kpa.
Determine the standard gibbs free energy change for the creation of methane from carbon and hydrogen at 298 k.
And the change in gibbs free energy is equal to the enthalpy change for the reaction minus the temperature at which it is occurring times the change in entropy.
The gibbs free energy of a system at any moment in time is defined as the enthalpy of the system minus the product of the temperature times the entropy of the system.